Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miyahara, Kaname; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Nakayama, Shinichi
IAEA-CN-211 (Internet), 2 Pages, 2013/01
After the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear accident, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was chosen by the Government to conduct decontamination pilot projects at selected sites in Fukushima prefecture. Despite tight boundary conditions in terms of timescale and resources, the demonstration projects have served their primary purpose of development of a knowledge base to support more effective planning and implementation of stepwise regional remediation of the evacuated zone. A range of established, modified and newly developed techniques have been tested under realistic field conditions and their performance characteristics determined. The results of the project can be summarised in terms of site characterisation, clean-up and waste management.
Yamagishi, Isao; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Terada, Atsuhiko; Kamiji, Yu; Kato, Chiaki; Morita, Keisuke; Nishihara, Kenji; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Ji, W.*; Fukushima, Hisashi*; et al.
IAEA-CN-211 (Internet), 5 Pages, 2013/01
Since the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, a large amount of radioactive contaminated water has been generated to cool damaged reactor cores. Adsorption of cesium with zeolite-like media was employed for treatment of this contaminated saline water. As spent zeolite media are highly radioactive, their safe storage is a pressing issue. Japan Atomic Energy Agency has extensively conducted R&D on the management of secondary wastes produced by the operation of the treatment system. Subjects on the safe storage of spent zeolites include the analysis of their characteristics and the evaluation of effectiveness of the present safety measures in consideration of decay heat emission and hydrogen generation by water radiolysis as well as durability of vessels exposed to saline. Preliminary results obtained are described in the present paper.
Nakayama, Shinichi; Miyahara, Kaname
no journal, ,
In decontamination pilot projects conducted by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), under contract with the Japanese Government, many different techniques were tested to determine their applicability to remediate areas evacuated after the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear accident of March 11, 2011. In addition to buildings, roads and forest adjacent to living areas, farmland was one of the main decontamination targets and is the focus for this paper. Information on applicable methods/technologies, procedures, machinery, cost, as well as decontamination effects by each methods/technologies were analyzed, and as a result recommended cleanup approach was indicated.
Okumura, Masahiko; Akasaka, Koichiro*; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Miyahara, Kaname; Nakayama, Shinichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Kitagaki, Toru; Wakui, Ryohei; Higuchi, Hidetoshi; Koizumi, Kenji; Yano, Kimihiko; Kaji, Naoya; Washiya, Tadahiro
no journal, ,
Nakamura, Masahiro; Takahatake, Yoko; Watanabe, So; Koma, Yoshikazu; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Nakajima, Yasuo
no journal, ,
In the emergency cooling procedure of the reactor vessel of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, massive amount of radioactively contaminated water containing salt was generated due to the injection of seawater as a countermeasure against fuel meltdown. This contaminated water has been processed for re-use as reactor coolant by zeolite adsorption, precipitation and desalination. Extensive analysis of the water revealed that major radioactive nuclides contained are 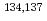 Cs and
Cs and  Sr of fission products accompanied with some activation products including
Sr of fission products accompanied with some activation products including  Co and
Co and  Mn. In order to establish a decontamination system of water resulting from a severe nuclear accident, an efficient decontamination process of nuclides above mentioned is required. A new decontamination process, which consists of simultaneous decontamination of radioactive transition metals and Cs by ferrocyanides precipitation together with titanium oxide adsorption for Sr decontamination is investigated.
Mn. In order to establish a decontamination system of water resulting from a severe nuclear accident, an efficient decontamination process of nuclides above mentioned is required. A new decontamination process, which consists of simultaneous decontamination of radioactive transition metals and Cs by ferrocyanides precipitation together with titanium oxide adsorption for Sr decontamination is investigated.
Sekio, Yoshihiro; Yamagata, Ichiro; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Sasaki, Shinji; Ogawa, Ryuichiro; Mashiko, Shinichi; Hayashi, Takehiro; Inoue, Toshihiko; Inoue, Masaki; Maeda, Koji
no journal, ,
Corrosion and mechanical property tests utilizing spent fuel cladding made of zircaloy-2 were performed as a tentative test of the project for the purpose of simulating an environment at the very early stage after the accident in the SFP of unit 4 in the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant. The result of metallurgical investigation after corrosion test showed that no obvious changes in oxide film formed on the outer surface of cladding such as stripping occurred. In addition to that, the ring-tensile test results of samples after corrosion test was obtained and compared with that of samples before corrosion test, indicating that no significant degradation in mechanical property was confirmed. These results would have indicated that integrity of FAs was kept to be high as same as what it was before conducting corrosion test.